COMPUTER CLASS 10TH
CH1:-PROGRAMMING TECHNIQUES
Q1. Select the best
answer for the following MCQs.
i. Which of the following structures repeats one or more
operations.
A. Sequence
B. Section
C. Loop
D. Decision
Correct answer is Loop.
ii. Which of the following structure allows a choice among various options?
A. Sequence
B. Section
C. Loop
D. Decision
Correct
answer is Selection.
iii. Which of the following is a sequence of instruction written
in a computer language to solve a problem?
A. Algorithm
B. Flowchart
C. Program
D. Program Analysis
Correct answer is Program.
iv. What illustrate a sequence of operation to be performed to
solve a problem in the form of a diagram?
A. Algorithm
B. Flowchart
C. Program
D. Program Analysis
Correct
answer is Flowchart.
v. What is represented by parallelogram in a flowchart?
A. Input/ Output
B. processing
C. Start/Stop
D. Decision
Correct
answer is Input/Output.
vi. What is represented by a small circle in a flowchart?
A. Start/Stop
B. Decision
C. processing
D. Connector
Correct
answer is connector.
vii. Which symbol is used for decision in flowchart?
A. Rectangle
B. parallelogram
C. diamond
D. Oval
Correct
answer is Diamond.
viii. Which symbol is used for processing in a flowchart?
A. Rectangle
B. Parallelogram
C. Diamond
D. Oval
Correct
answer is Rectangle.
***
Q2. Write short answers of the following questions.
Q1:Define Computer.
ANS:- computer:- A computer is a general-purpose electronic Machine invented to help people solve various Problems. Computer must be programmed by Human beings to perform various tasks. Various Programming techniques are used for solving Problems on computer.
Q2:What is Algorithm and what is the role of algorithm in problem
solving?
ANS:- Algorithm:- • Algorithm means method, procedure, technique or plan.
• Algorithm is a step-by-step problem solving method
that is easy to understand and follow.
• It is a set of steps that clearly defines a sequence
of operations to solve a problem.
Role
of Algorithm in problem solving:-
• Algorithm plays an important role in computer programming.
• Computer programming is the process of taking an
algorithm and coding it in a programming language.
• Formulating an algorithm is the first step for
developing a computer program.
Measuring
Efficiency of an Algorithm:-
If
Efficiency of an Algorithm, Will be move Efficient
• Minimum usage of resources.
• Minimum usage of time taken by Program/Problem.
• Minimum usage of Storage/Space.
Q3: What is Flowchart?
ANS:- Flowchart:- • Flowchart is a diagrammatic representation of algorithm.
• Flowchart describes what operations are required to
solve a given problem.
Importance
of Flowchart in Problem Solving:-
Flowchart illustrates the sequence of operations to be performed to solve a given problem in the form of a diagram. Computer programmers draw flowcharts before writing computer programs. It provides an easy way to analyze and find solutions of problems. It is very easy to write the program in any high
level language. It is very helpful in communicating
about problem solving method to othes. It also helps in finding and removing errors
in computer programs.
Steps for
Drawing Flowchart:-
The flowchart developer must
determine the following requirements before drawing a flowchart.
• Input to the
flowchart
• Type of
processing required
• Decisions to
be taken
• The output to
be produced after processing
Flowchart Symbols:-
• Flow Line
• Start/Stop
• Input/ Output Process
•Process Process
• Decision
• Connector
Q3:- What are the advantages of using flowcharts?
ANS:- Advantages of using
Flowchart:-
• Flowchart
illustrates the sequence of operations to be performed to solve a given problem
in the form of a diagram.
• Computer
programmers draw flowcharts before writing computer programs.
• Flowchart
provides an easy way to analyze and find solutions of problems.
• Flowchart is
very easy to write the program in any high level language.
• Flowchart is
very helpful in communicating about problem solving method to othes.
• Flowchart also
helps in finding and removing errors in computer programs.
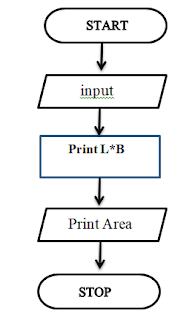
Q5:- Draw any four graphical symbols used in Flowchart and Explain
them.
ANS:-
Flowchart Symbols:-
• Flow Line
• Start/Stop
• Input/Output
• Process
• Decision
• Connector
Flow Line:- It is arrow used to connect various flowchart symbols and indicates the flow
of control in the flowchart.
Start/Stop Symbol:- It is a rounded rectangular shaped symbol. It is used to indicate the
tart or end of a flowchart. We can only write the words
Start or Stop inside this symbol.
Input/ Output Symbol:- Parallelogram represents input or output operations in a flowchart.
It contains the word INPUT along with the variables for input operation OUTPUT along with
the output data for output operation.
Process Symbol:- A rectangular block is used for any data processing operation. All
the calculations appear inside the processing symbol,
Example:- "SUM= A + B". Variables
are also initialized inside the process symbol, such as “K=1”.
Decision Symbol:- A diamond shaped symbol represents decision in a flowchart and it
contains a condition. The words TRUE or FALSE can also be
used instead of YES or NO.
Connector Symbols:- These symbols are used to connect one part of a flowchart to the
other on the same page (On-Page connector) or on the new page
(Off-Page connector).
***
Q3.Write
long answers of the following.
Q3:-Describe the steps involved in Problem
solving.
ANS:- understanding the problem:- Solving problems is the main task of computer Science. which is the job of computer programmer. Programmer must first understand how a human solves a problem then translate it into a set of instructions in a programming language that a computer can understand and execute.
The following steps are involved in
problem solving on the computer.
Defining the problem:-
Defining the problem is
initial stage of problem solving. It is very important to understand
the problem before the programmer starts working on its solution.
The following are the steps to properly define and understand the problem.
• Carefully read the problem to understand what it tells.
• Find out what the problem asks to do.
• What information can be obtained from the problem?
• What is required to be calculated as the solution of the problem?
Analyzing the problem:-
At this stage of problem solving, the programmer investigates the problem and gathers as much information as possible to find a solution. The following questions are to be asked to analyze the problem.
• Is it possible to solve the problem on a computer?
• What is to be done to find the solution of the problem?
• What is the proper sequence of steps to solve the problem?
• What are the inputs and what output is required?
• How many solutions are possible?
• Which solution is the best and why?
• How solution will be implemented?
• What is the formula to find the average marks?
Planning
the solution of the problem:-
Planning the solution of the problem is a creative stage of problem solving. It refers to dividing the solution into steps and arranging them into proper order that will solve the problem.
• Talk to the right person. The person you speak must have the ability to resolve the issue
• Focus on talking about the problem with the product or service, rather than taking issue with a person.
• Stay calm and reasonable. Explain the problem in detail and provide any evidence you may have.
• Tell them what outcome you want. It is the store or service provider’s responsibility to resolve the problem, but it can be helpful to ask them for a specific solution.
Candid
solutions of a problem:-
All
the possible solutions of a problem that produce correct result are known as
candid solutions. To find candid solutions of a problem, programmer has
to look for different methods to solve the problem and come up with
several solutions.
Select the best solution:-
After finding the candid solutions, only one solution can be selected. The selection of
final solution of a problem should be based on the following criteria.
Speed:- The selected solution of the problem should be efficient. In other words, it means
when the solution is implemented in a programming language, the
program should run fast.
Cost:- The selected solution of the problem should provide a cost-effective way of
implementation.
Complexity:- The selected solution of the problem should not be complicated. It should
contain minimum number of instructions/simple steps.
Q3.Write long answers of
the following.
Q4:- Write an Algorithm
to calculate the area of rectangle for given breath and length.
ANS:-
Step1: Input the width and length in inches(LI)
Step2: calculate the
length in CM by Multiplying Land M
Step3: Print A
Q5:- Write an Algorithm
that input length in inches and calculate and print it in centimeters.
ANS:-
Step1: Input the length in inches
Step2: Check the length in cm (LCM) by multiplying LI
with 2.54
Step3: Print LCM
Q6:- Write an Algorithm
that input marks and then print the message “PASS” and “FAIL”. Passing marks
are 33.
ANS:-
Step1: Input Marks
Step2: check if (M<33) then print “FAIL” GOTO step4
Step3: ELSE print “PASS”
Step4: Stop
Q7:- Write an Algorithm to
find SUM of given sequence.
SUM=20+25+30+35+40+45+50+55+60
ANS:-
Step1: Start
(i) SUM+0,k=20
Step2: ADD K to SUM
SUM=SUM+K
Step3: Increment K by 5
K=K+5
Step4: check if value of K is less or equal to 60
IF K<= 60 THEN GOTO STEP2 otherwise GOTO step5
Step5: print SUM
Step6: Stop
Q8:- Write an Algorithm to
find PRODUCT of given sequence.
PRDUCT=1x3x5x7x9x11x13x15
ANS:-
Step1: Start
(i) k+1,prod=1
Step2: increment K by 2
K=K+2
Step3: find the prod
Prod=prod x K
Step4: check if value of K is less or equal to 16
IF K< 16 THEN GOTO STEP2 otherwise GOTO step5
Step5: print prod
Step6: Stop
Q9:- Write an algorithm
to print multiplication table of a number in reserve order.
ANS:-
Step1: enter number
(i) I with 10
Step2: find the prod of N and I
prod=N+I
Step3: print N, I and prod
Print N, I and prod
Step4: decrease k value I by 1
I = I - 1
IF I >0 THEN GOTO STEP3 otherwise GOTO step6
Step5: Stop
Q10:- convert the
algorithm to print questions Q4 to Q9 to flow chart.
ANS:-
Q6:- Write an Algorithm that input marks and then print the message “PASS” and “FAIL”. Passing marks are 33.
Q7:- Write an Algorithm to find SUM of given sequence.
SUM=20+25+30+35+40+45+50+55+60
Q8:- Write an Algorithm to find PRODUCT of given sequence.
PRDUCT=1x3x5x7x9x11x13x15
Q9:- Write an algorithm to print multiplication table of a number in reserve order.
***
CH2:-PROGRAMMING IN C
Q1. Select the best
answer for the following MCQs.
i. What define the rules of valid statement
in programming?
A. Compiler
B. Interpreter
C. Styntax
D. Semantic
Correct answer is Syntax.
ii. Which
language is directly understood by the computer?
A. Machine language
B. Assembly language
C. High level language
D. C language
Correct answer is Machine language.
iii. When was c
language developed?
A. Late 1960s
B. Early 1970s
c. 1980s
D. 1990 Correct answer is Early 1970s.
iv. Who
developed java language?
A. Dennis
Ritchie
B. Microsoft
C. Sun
Microsystems
D. IBM Correct answer is Sun Microsystems.
V. What is the other
word used for reserved words?
A. Compiler
words
B. Keyboard
C. Special programming
words
D. Mnemonics
Correct answer is Keywords.
vi. How many
bytes are set aside by the compiler for a variable of type int?
A. 2
B. 3
C.4
D. 5
Correct answer is 2.
vii. How many
bytes are set aside by the compiler for variable of type float?
A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
Correct answer is 4.
viii. What is
the range of numbers that can be stores in a variable of type double float?
A. -32,768 ~ + 32,767
B. 10^-38 ~ 10^38
C. 10^-308 ~ 10^308
D. 10^-4932 ~ 10^4932
Correct answer is 1^-308 ~ 10^308.
ix. Which
program translate high level language in to machine level language?
A. Compiler
B. Linker
C. Loader
D. Debugger
Correct answer is Compiler.
x. Which
software helps in finding and removing errors in programs?
A. Linker
B. Text editor
C. Loader
D. Debugger
Correct answer is Debugger.
***
Q2. Write short answers of
the following questions.
Q1:Define
computer program.
ANS:- computer program:- A computer program is a set of
instructions written in programming language to solve a particular problem
and achieving specific results. Any task performed by a computer is controlled
by a set of instructions that are executed by the microprocessor. A large
variety of programming languages have been developed for writing computer
programs to use the computer as a problem-solving tool.
Each statement of a programming
language has syntax and semantic.
Syntax:- Syntax refers to the rules of a
programming language according to which statements of a program are to be
written. It describes the way to write correct statements in a program.
Syntax of a programming language is similar to the grammar of a natural
language.
Example:-
variable + expression;
Semantic:- Semantic gives meaning to
statements of a programming language. It describes the sequence of operations
to be performed by a computer when executing the statements of a computer
program. The values stored in variables a and b and then
store the result in variable sum.
Example:-
sum = a + b;
Q2: Different
between syntax and semantic.
ANS:-
Syntax:- Syntax refers to the rules of a
programming language according to which statements of a program are to be
written. It describes the way to write correct statements in a program.
Syntax of a programming language is similar to the grammar of a natural
language.
Example:-
variable + expression;
Semantic:- Semantic gives meaning to
statements of a programming language. It describes the sequence of operations
to be performed by a computer when executing the statements of a computer
program. The values stored in variables a and b and then
store the result in variable sum.
Example:-
sum = a + b;
Q3:
write three different between assembly language and HLLs.
ANS:-
|
Assembly language |
High level languages (HLLs) |
|
•Assembly level language s are not easy to understand.
Because they consist of symbolic codes or abbreviations know as mnemonics. |
•High level language is easy to use, understandable and
less prone to errors. |
|
•The programs written in Assembly level languages are not
very easy. |
•The programs written in HLLs level languages are very
easy. |
|
•Assembly level language are difficult to use. Programs
written in symbols or special character. |
•High level languages are not machine dependent. They
enable program in any language such as English. |
Q4:
Write four characteristics of HLLs.
ANS:-
•High level language is easy to use, understandable and less
prone to errors..
•The programs written in HLLs
level languages are very easy.
•High level languages are not
machine dependent. They enable program in any language such as English.
• program written in high level
language must translate in to machine language.
•High level language program are
highly structured.
Q5:
Define integrated development environment (IDE).
ANS:- integrated development environment (IDE):- Most of the new programming languages use integrated
Development Environment (IDE) to create compile and run programs. IDE is a
computer software that brings all process tools require from program
development in one environment. IDEs aim is to make three life of programmers
simple easy by grouping together, all task needed for built application in to
one Environment. Today modern IDEs have user-friendly Graphical user interface
(GUI).
Q6:
Different between constant and variable.
ANS:-
Constants:- Constants are quantities whose
values do not change during program execution. They may be numeric,
character or string. Numeric Constants are of two types, integer and
floating-point numbers
Example:-
Integer constants represent values
that are counted, like the number of students in a class, integer constants are
7145, -234, 26, etc.
Example:-
Floating-point constants are used
to represent values that are measured
Example:-
Character Constant is one of the
symbols in C character set.
Example:- String Constant contains a string of characters within double
quotes such as “Hello Ahmed”.
Variable:- A variable is a symbolic name that
represents a value that can change during execution of a program. A variable
has a name, known as variable name and it holds data of other types. A
number or any other type of data held in a variable is called its value. Variables
are of two types, numeric and character.
Example:- Numeric variables are used to
represent numeric values in computer programs. sum, avg, length, marks, etc.
Example:- Character variables represent
character values in computer programs. It can represent a single
character or a string of characters. Some examples of character variables are
name, city, gender, etc.
Q7:
Which of the following are valid C variable? Give the reasons if not valid
variable.
Area, 5x, sum, net pay, float, _age, else,
case, size22, my_ weight
|
variables |
If
valid/ not valid |
Reason |
|
area |
valid |
Due
to use as variable |
|
5x |
Not
valid |
Due
to start number |
|
sum |
valid |
Due
to use as variable |
|
net
pay |
Not
valid |
Due
to Space b/n |
|
float |
Not
valid |
Due
to data type |
|
_age |
Not
valid |
Due
to special character |
|
else |
Not
valid |
Due
to command |
|
case |
Not
valid |
Due
to command |
|
Size22 |
valid |
Due
to use as variable |
|
My_
weight |
valid |
Due
to use as variable |
Q8:
What are reserved words? Why should not be as a variable name?
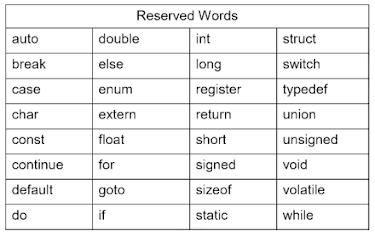
ANS:- Reserved words:- The words that are part of programming language and have special purpose in computer programs are called reserved words are keywords. They have predefined use and cannot used as any other purpose. Reserved words are written in lowercase letters. There are 32 words used as reserved words in C.
Q9: Why comments are used in programs?
ANS:- it
is good programing practice to add comments in program to make it easy for
others to understand it. Comments in the source code are ignored by compiler.
Comments are add in program when the fact is necessary to be brought to their
attention of program’s reader there are two types of comments
Single
line comment “ \ ”
Multiple
line comment “ *\ ”
Q10:
what is the purpose of header files in C languages?
ANS:- C language contain numbers of standard function in library file that perform various task in C program. These task include all input/output operations and all the math operations. Library file contain header file and each file contain a set of functions. Some commonly used header files are stdio.h, conio.h, maths.h.
Q3: Describe the following High level:-
ANS:- C/C++:-
C language was developed in early 1970s by Dennis Ritchie at Bell
Laboratories. C has become one of the most popular programming languages today.
It is a highly structures programming language that is easy to understand and
use. In the past, it was mainly used for writing system programs such as
operating systems, compilers, assemblers, etc. Today, it is used for writing
all types of application programs as well, such as word-processing programs,
educational programs, games, etc.
C++ was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup also at Bell
Laboratories during 1983-1985. C++ is a superset of C, meaning that any valid C
program is also a valid C++ program. The purpose of developing C++ was to
provide programming facilities to easily and quickly write more powerful
programs.
Visual Basic:- Visual Basic (VB) is a high level language which evolved
from the earlier version called BASIC. BASIC stands for Beginner’s All-purpose
Symbolic Instruction Code. VB is a very popular programming language for
writing Windows and Web applications. It provides a graphical development
environment to programmers to develop Web applications. The user can also write
programs related with engineering, science, education etc.
C#:- C# (pronounced as C-sharp) is a language developed in 2000 by
Microsoft Corporation. It is a simple, modern, general-purpose programming
language. Syntax of C# is very similar to C and C++. It also has some features
of Java. It is a language that makes computer programming easy and efficient.
It provides facilities to write Web applications that can be used across the
Internet. All types of programs including games, utilities, operating systems,
compilers, business applications and Web based applications can be developed in
C#.
Java:- Java is a high-level language developed by Sun Microsystems. It is very similar in syntax to C and C++. In Java, the user can write all types of programs by using java. Java is an ideal language for network computing. It is widely used in Web applications. The current versions of most of the Web browsers are made Java enabled. A few browsers that support Java are Microsoft’s Internet Explorer, Firefox etc.
Q4: What is C language IDE? Explain its modules in detail.
ANS:- integrated development environment
(IDE):- Most of the new programming
languages use integrated Development Environment (IDE) to create compile and
run programs. IDE is a computer software that brings all process tools require
from program development in one environment. IDEs aim is to make three life of
programmers simple easy by grouping together, all task needed for built
application in to one Environment. Today modern IDEs have user-friendly
Graphical user interface (GUI).
IDEs Modules:- C language IDE consists of the following
modules.
• Text
Editor
• Compiler
• Linker
• Loader
• Debugger
Text Editor:- A text editor is a simple
word-processor that is used to create and edit source code of a program. Files
created by a text editor are plain text files. Most of the editors
automatically highlight compile errors to simplify removing them.
Compiler:- A compiler is a software that
translate (C) source program in to
object program that can understood and execute by computer. It also find syntax
errors and give hints to correct them.
Linker:- Linker
is a software that translate object program into single executable program. .
It will replace this function in the object program with the code from C
library and then create a single executable program.
Loader:-
It is a software that loads programs
into memory and then executes them.
Debugger:-
It
is a software that executes a program line by line, examines the values stored
in variables and helps in finding and removing errors in programs.
Q5: what are the rules for specifying a
variable name in C language?
ANS:- • A variable begins with a letter or underscore
( _ ) and may consist of letters, underscores and/or digits.
• The underscore may be used to improve
readability of the variable name. For example, over_time.
• There is no restriction on the length of a
variable name. However, only the first 31 characters of a variable are
significant. This means that if two variables have the same first 31 characters
they are considered to be the same variables.
• Both upper and lower case letters are allowed
in naming variables. An upper case letter is considered different from a lower
case letter. For example the variable AVG is different from Avg or avg.
• Special characters cannot be used as variable
name. e.g., #, ?, @ etc.
• Reserved words of C language such as int,
case, if, etc., cannot be used as variable names.
• Space is not allowed in the name of variable.
For example ma ss is not correct.
Q6: What
is a preprocessor directives? Explain
#include processor directive in detail.
ANS:- a preprocessor directives:- Preprocessor
directives are instructions for the C compiler. Every C language program
contains certain preprocessor directives at the beginning of the program.
Before translating a C language program into machine language, the compiler of
C language carries out the processor directives. These directives start with
number sign (#). The most commonly used preprocessor directives are #include
and #define. #include
#include<header file name>
When this
preprocessor is carried out by the C compiler, it will search for the header
file that is written within the less than (<) and greater than (>)
symbols and copy it into the source file. the header file stdio.h is used. It
tells the C compiler to copy the stdio.h header file into the program. The
stdio.h header file stands for standard input-output header. It includes the
standard printf( ) and scanf() function prototypes. In the above program the
printf() functions is used.
main()
Function:- C programs consist of one or more functions. A function
performs a single well-defined task. Every C program must have the function
main() which is the first section to be executed when the program runs. The
general form of main() is: void main(void).
Body
of main() Function:- The body of the function main() is surrounded by braces
(curly brackets { and }). The left brace indicates the start of the body of the
function and the matching right brace indicates the end of the body of the
function.






Helpful content
ReplyDeleteHelp thanks sir
ReplyDeleteEasy to learn thanks 👍
ReplyDeleteVery awesome notes
ReplyDeleteHelpful sir
ReplyDelete